What is a Student Loan ?
A student loan is a form of loan that is aimed to assist students in paying for post-secondary education and associated fees such as tuition, textbooks and other materials, and living expenses. It may differ from other forms of loans in that the interest rate is significantly lower and the schedule of payments can be postponed while the student continues to attend in school. Many countries also have strong regulations governing renegotiating and bankruptcy. The contrasts in the student loan systems of numerous major countries are highlighted in this article.
A student loan is a sum of cash that is borrowed to pay for postsecondary education or higher learning-related expenses. Education loans are designed to pay the costs of tuition, textbooks and other materials, and living costs while the applicant is pursuing a degree. Payments are frequently deferred while students are enrolled in college, and depending on the lender, payments may be deferred for a further six months after graduation. Although there are many different types of education loans, they can be divided into two categories: federal loans (supported by the government of the United States) and individual loans.
How a Student Loan Works ?
Students who request for a student loan do not have to pay the entire sum right away; the payback period begins months or years after the course is completed. It can even be expanded from five to seven years in exceptional situations.
The rate of interest varies according on the bank. The bank pays the loan amount immediately to the educational institution/university at the beginning of the semester. Education loans also cover every other cost, such as librarian fees, dormitory fees, book costs, laboratory fees, and so on, ensuring that the student is not responsible for any out-of-pocket expenses.
Student loans are provided for for the reason of pursuing an academic degree at a recognized institution or university. Student loans can be received from the federal government or from commercial lenders. Federal loans frequently have reduced rates of interest, and some even have interest that is subsidized. For applicants, private-sector loans often follow a more standard lending process, with rates that are normally higher than the government’s loans.
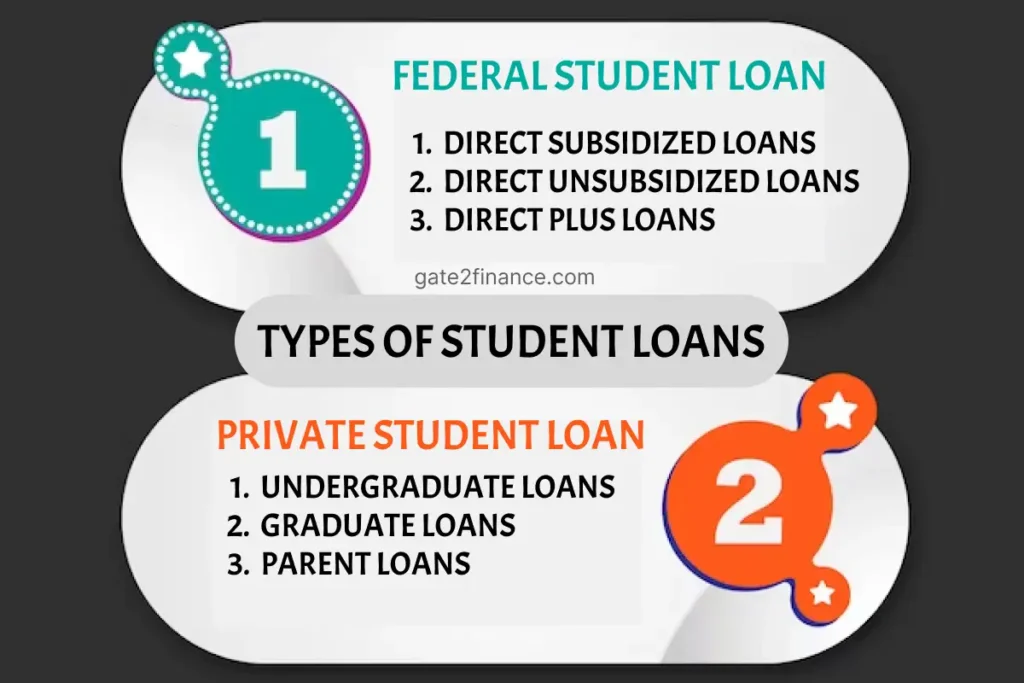
Federal student loans
While there are numerous methods for paying for college, federal student loans are among the most common. These loans include flexible methods of payment and low interest rates. There are several loan options available under the federal Direct Loan Programme.
Direct Subsidized Loans
Students in undergraduate programmes who have proved financial need are eligible for Direct Subsidised Loans. These loans do not accumulate interest while the applicant is enrolled in school, within the 6 month grace period, or during any subsequent deferment term.
Direct Unsubsidized Loans
Direct Unsubsidized Loans are available to college, graduate, and professional students. Borrowers are not required to demonstrate financial necessity, but interest is charged on these loans immediately. This means you’ll be charged interest while in school, after graduation, and throughout times of deferral and forbearance.
Direct PLUS Loans
Graduate or professional students, as well as parents of needy undergraduate students, can apply for Direct PLUS Loans to help pay for education expenditures. Direct PLUS Loans have higher rates of interest and origination costs than Direct Subsidised and Unsubsidized Loans.
Parent PLUS loans, unlike regular federal student loans, are taken out directly by parents. While students can make repayments on their own, their parents are legally and financially liable for repaying the entire sum of their parent PLUS loans. Only the parent’s credit report will be affected by the loan, not the student’s.
Private student loans
Sallie Mae, Discover, and Citizens Bank are among the most well-known private student loan businesses, but there are hundreds more. Private lenders provide a variety of repayment arrangements, incentives, and consolidation alternatives, as well as extremely cheap interest rates for qualifying consumers with strong or excellent credit. Private student loans, as opposed to federal student loans, can have either fixed or variable rates of interest.
Undergraduate loans
Private student loans for undergraduates frequently include flexible repayment options and may even provide borrowers with a principle reduction once they graduate. In contrast to federal student loans, bachelor private student loans frequently require a co-signer. A co-signer is a responsible adult who agrees to assume the entire liability for your student loans if you fail. Because undergraduates haven’t had time to build a credit history, individual lenders almost always demand co-signers.
Private undergraduate student loans typically have higher rates of interest than postgraduate student loans. They also typically have lesser loan amounts.
Graduate loans
Private lenders of student loans may provide personalized student loan choices for university, law school, medical school, and business school. Private financing for graduate or profession students are less likely than undergraduate loans to demand a co-signer. They frequently have greater loan amounts, longer repayment durations, and cheaper interest rates.
Private graduate student loans sometimes include characteristics tailored to the requirements of graduate school, such as extensive extensions of grace and in-school deferral periods, as well as extra time while students finish a residency.
Parent loans
Loans can be obtained by parents to assist pay for their children’s education. Parent loans, like conventional student loans, are available in both federal and private formats.
The parent PLUS loan is a popular government option. One significant advantage of the PLUS loan is that you can borrow the whole cost of your dependent’s attendance, minus any other financial aid. You must be a natural or adoptive parent of the dependent undergraduate, however stepparents may be eligible in specific cases. You must also have excellent credit and meet the normal federal student aid eligibility conditions, such as becoming a U.S. citizen or qualified noncitizen. The youngster must be enrolled as an undergraduate student at a suitable institution at least half-time.
Parents could also check into private student loans to determine if they qualified for a lower interest rate. For loans issued on or after July 1, 2023, but before July 1, 2024, the present direct PLUS interest rate is 8.05%. It has a set interest rate. Private student loans can have interest rates ranging from 4 to 15%, and some may have rates that are variable.
Why Take Student Loan?
Almost every Indian parents now place a high value on their children’s education. Using family cash, borrow from relatives and close friends, selling assets, or taking out a student loan are all common ways of funding higher education. It was previously considered that only those in the middle income bracket used education/student education loans to fund their education.
With the benefits of an education loan becoming more apparent and specialists providing personal service, many wealthy households are now opting for an education loan and reaping specific perks such as:
- Students are given the option to assume financial responsibility.
- Keeping their family’s savings
- Creating a positive credit history
- Best choices for repayment
- A wide range of costs are covered.
- There is no loan obligation.
- Pursuing a dream course at their preferred college/university
Benefits of Student Education Loans
- Suitable for everyone: A student loan can be obtained by any student. Even the most disadvantaged members of society can obtain student education loans.
- This section applies to practically all courses in India, including graduate, post-graduation, certification courses, and vocational courses.
- Education loans are widely available, simple to secure, and a priority product in all banks, according to RBI standards.
- Loan amounts vary: Several banks and non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs) can provide loans ranging from Rs.40,000 to Rs.10 lakh for learning in India. The size of the loan, however, is determined by the course, college, and financial institutions asked for.
- As a result of inflation and changing costs, the expense of education is increasing. To minimise academic failures, student education loans are required.
- Benefits: Education loans include a bevy of supplementary benefits, such as covering library fees, laboratories fees, tuition, test costs, hostel fees, cash for books, devices, and uniforms, and travel expenses, among others.
- Easy repayment: Another important benefit of student education loans is that the loan volume allows for simple payback alternatives. If you’re still wondering how to receive a loan for school after 12th grade, check out Education Loan in India.









